Info
Subfamily: Panicoideae
Genus etymology: Paspalum = "millet" [Greek] some species are used as cereals
Species etymology: scrobiculatum = "minutely pitted" [Latin] supposedly refering to the lemma
Photosynthetic type: C4 (warm season)
Nativity: naturalized - accidental
First recorded in Hawaiʻi:
Legal status: USDA - noxious weed
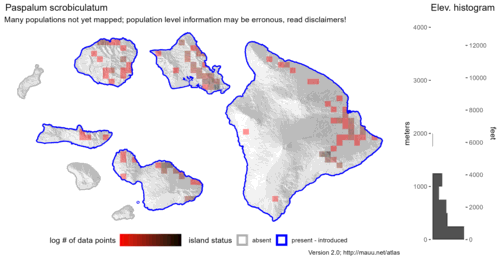
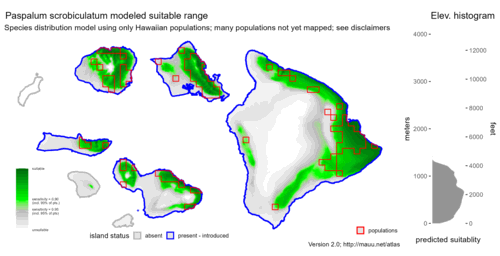
Map
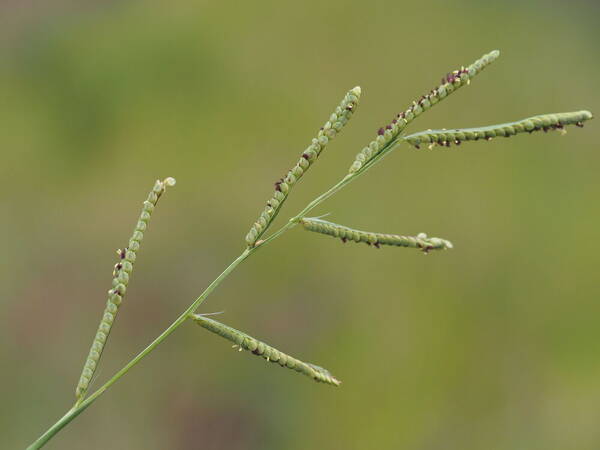
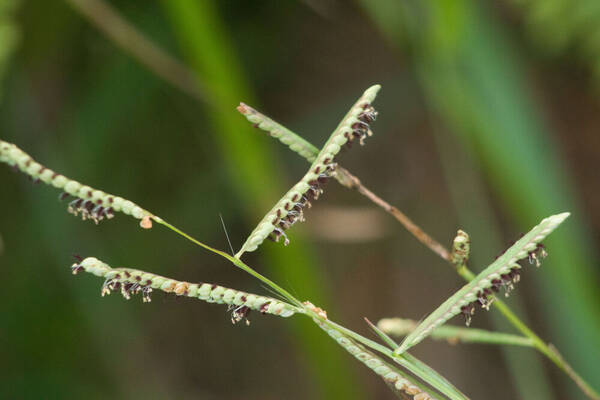
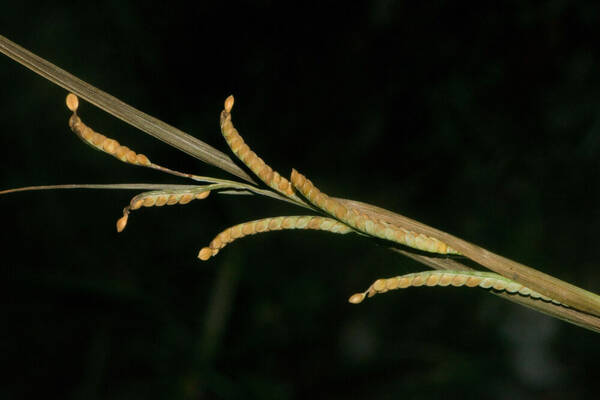
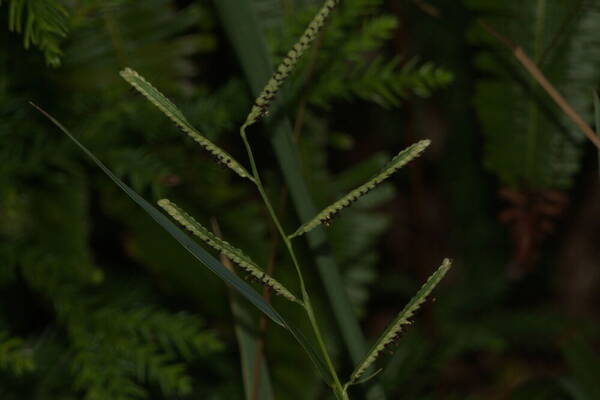
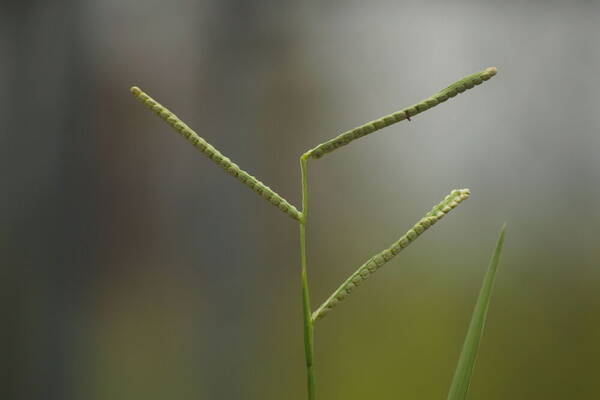
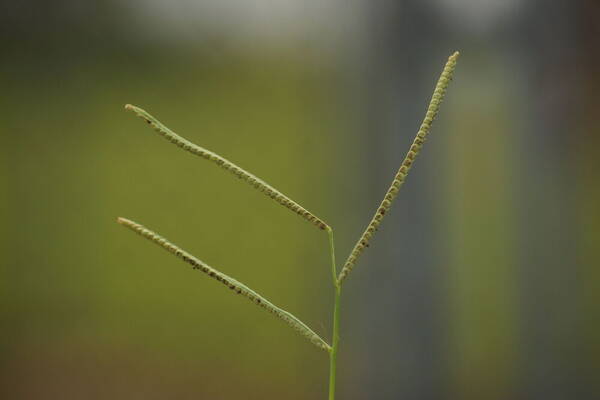
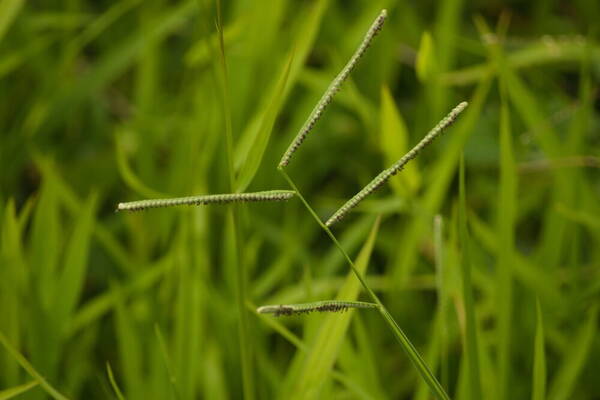
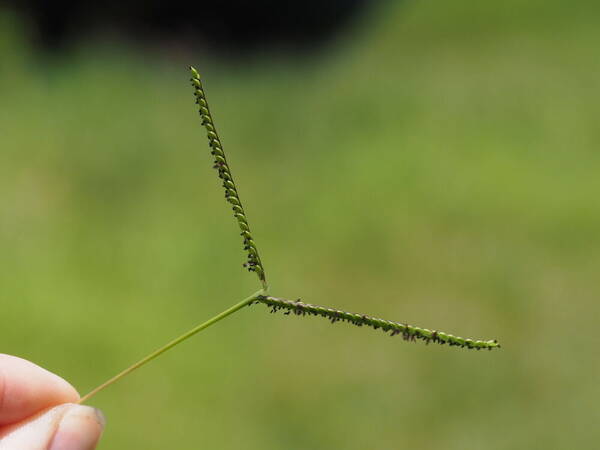
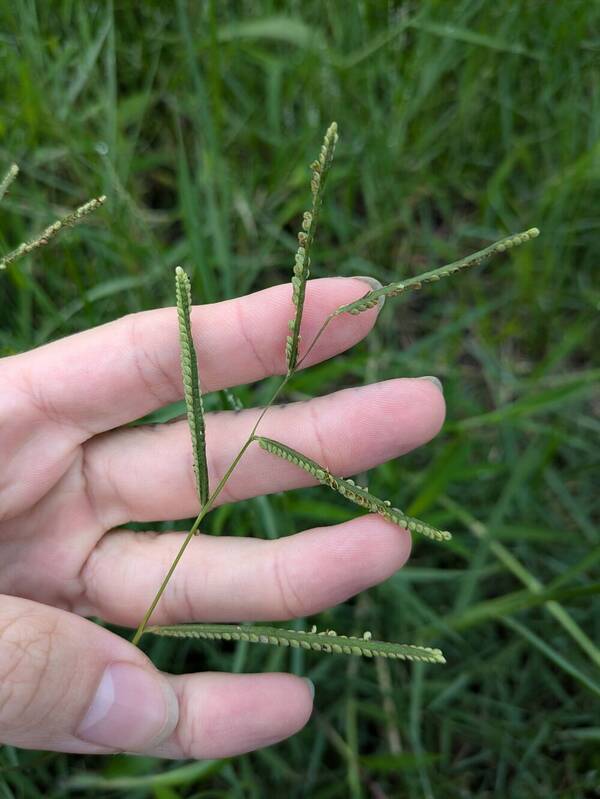
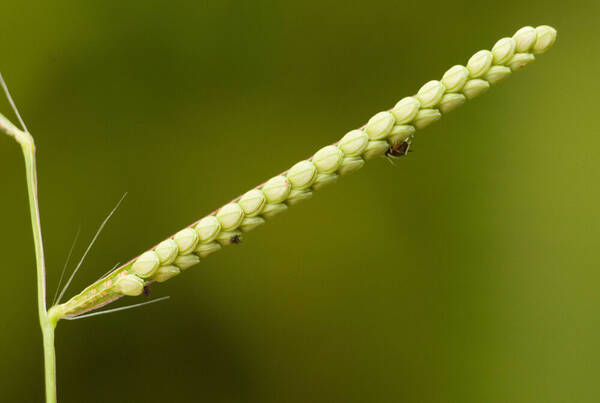
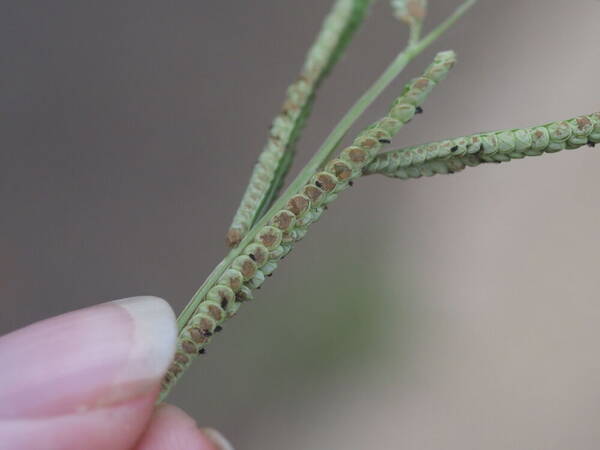
Inflorescence
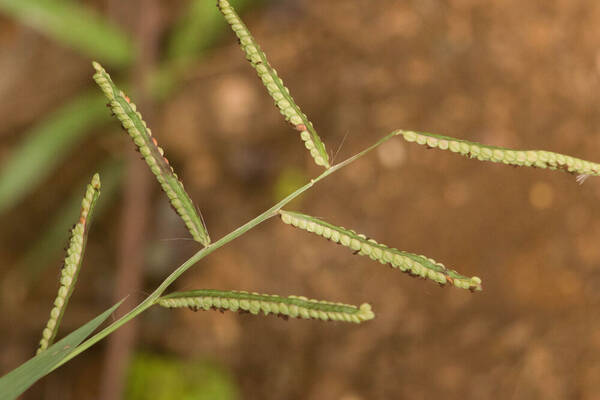
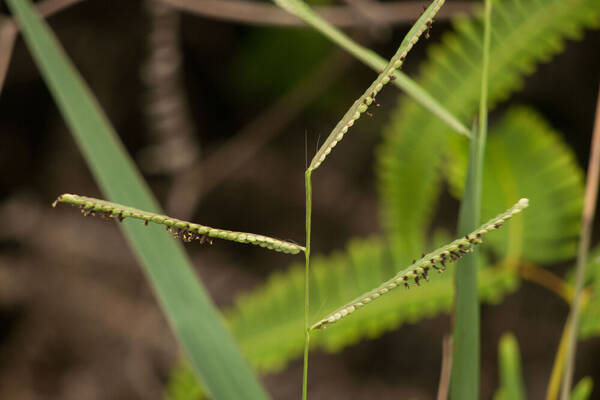











Plant
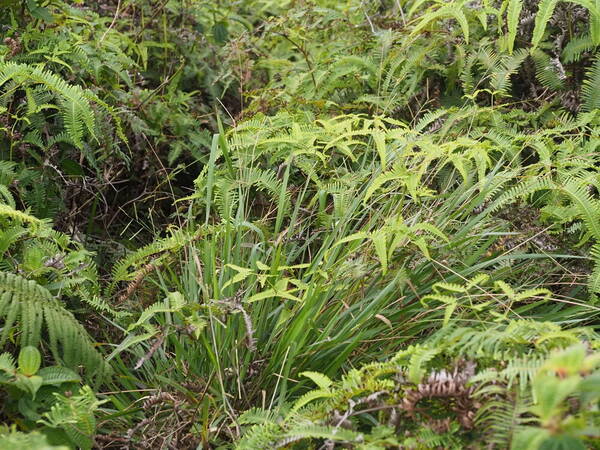
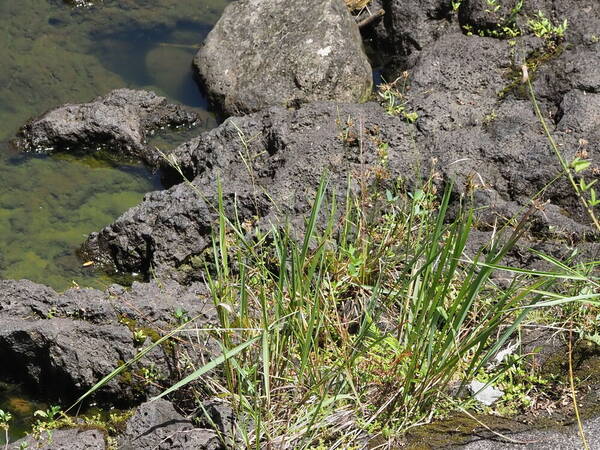


Habit
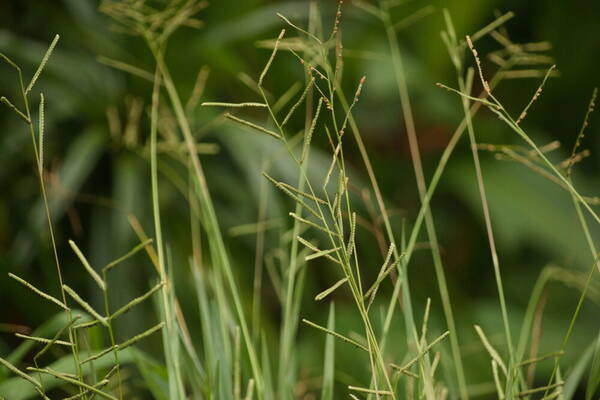

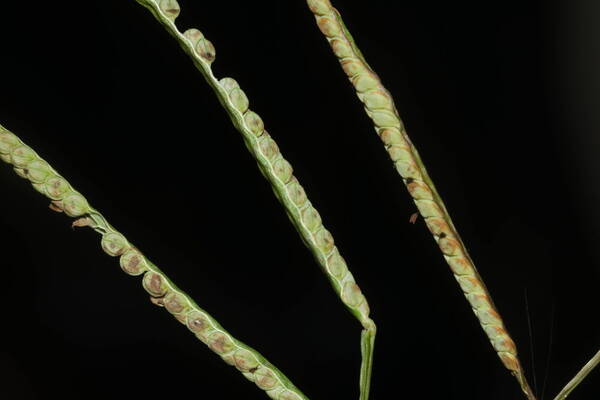
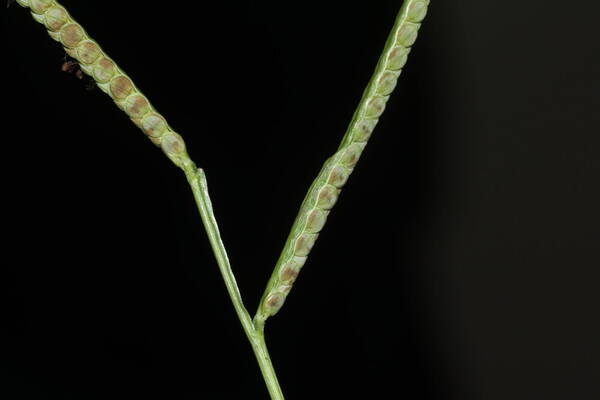
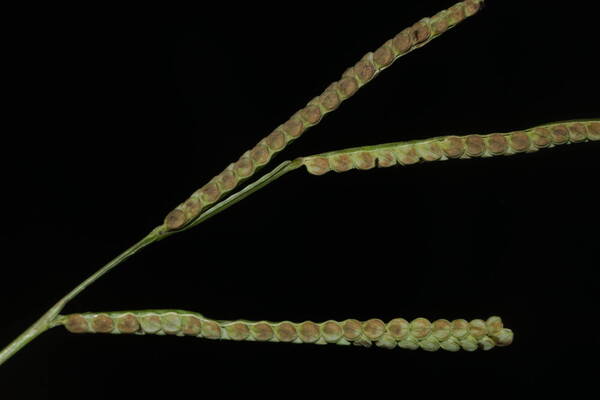
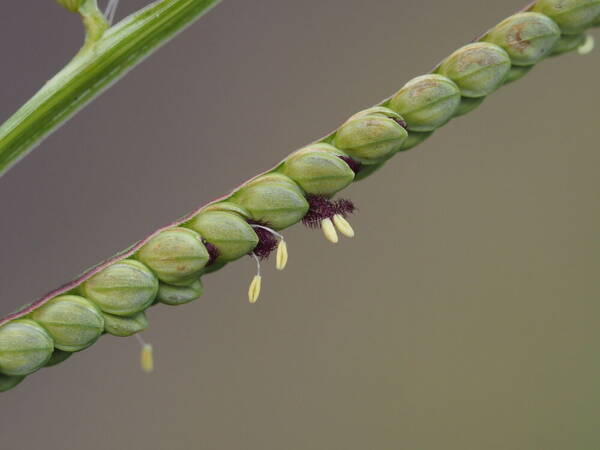
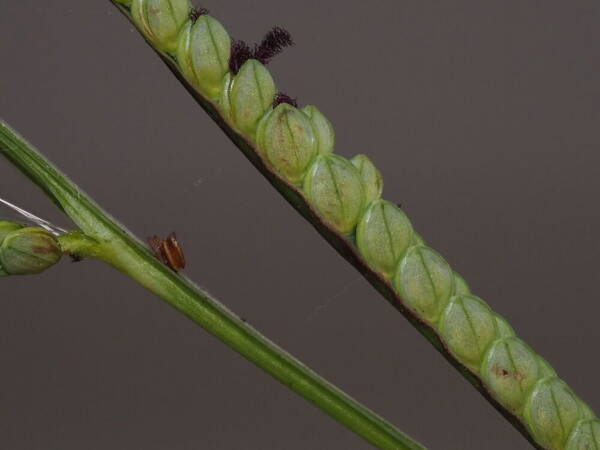
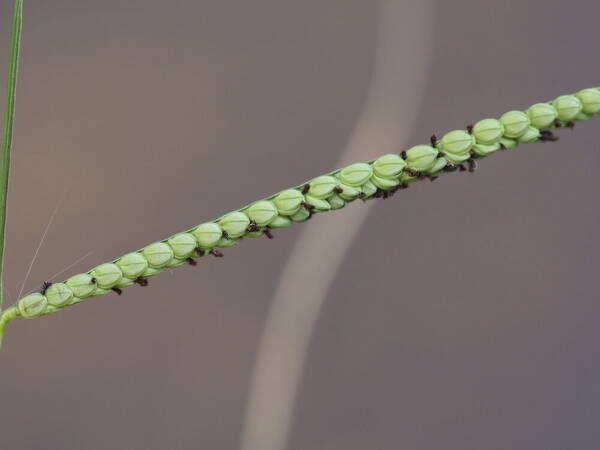
Spikelets
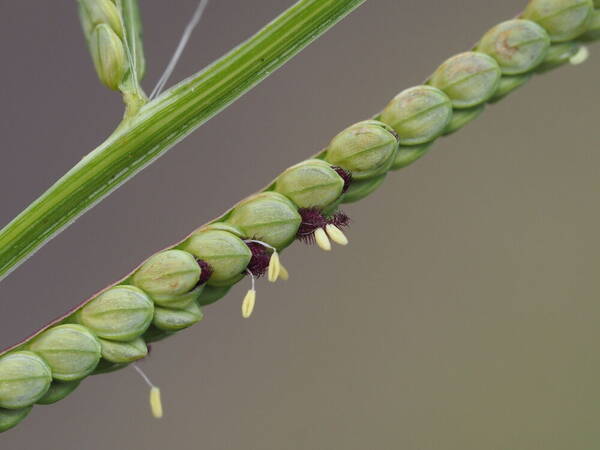









Description
Perennial; culms 10–150 cm. high, 1–6 mm. in diameter, 2–17-noded, the nodes commonly exposed, erect, or ascending from a decumbent base and rooting at the lower nodes. Leaf-blades linear, 5–40 cm. long, 3–15 mm. wide, tapering to a filiform tip. Inflorescence composed of 1–20 racemes, these digitate or borne on an axis up to 8 cm. long, the longest raceme 4–15 cm. long, with spikelets borne singly on a ribbon-like rhachis 1–2.5 mm. wide. Spikelets broadly elliptic, obovate or suborbicular, 1.4–3 mm. long, green becoming brown; lower glume absent; upper glume papery; lower lemma similar or rarely coriaceous, 3–5-nerved (in the latter case the nerves evenly spaced or the laterals close together); upper lemma finely striate, brown at maturity. Fig. 142.
(Description source: Clayton, W.D. & Renvoize, S.A. 1982. Flora of Tropical East Africa. Gramineae (Part 3). A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. 448 pp. )
Perennial. Culms 10–150 cm. high, 1–6 mm. in diam., the nodes mostly exposed, erect or ascending from a decumbent base and rooting at the nodes below. Leaf laminae 5–40 cm. long, 3–15 mm. wide, linear, tapering to a filiform apex. Racemes 1–20, digitate or borne on an axis up to 8 cm. long, the longest raceme 4–15 cm. long, the spikelets borne singly on a rhachis 1–2.5 mm. wide. Spikelets 1.4–3 mm. long, broadly elliptic to subrotund, green becoming brown. Inferior glume absent. Inferior lemma papery or rarely coriaceous, glabrous. Superior lemma brown at maturity.
(Description source: Launert, E. & Pope, G.V. (eds.). 1989. Flora Zambesiaca. Volume 10. Part 3. Kew, London. 152 pp. )
Plants annual. Culms 10-150 cm, erect or decumbent; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous; ligules 0.3-1.2 mm, often with a row of hairs behind them; blades 5-30 cm long, 2-8(12) mm wide, flat, usually glabrous. Panicles terminal, with 1-5 digitately or racemosely arranged branches; branches 3-10 cm, diverging to spreading, persistent; branch axes 1.5-3 mm wide, broadly winged, glabrous, margins scabrous, terminating in a spikelet. Spikelets 1.8-3.2 mm long, 2-2.3 mm wide, solitary, diverging from the branch axes, ovate, glabrous, olive green to dark, glossy brown. Lower glumes absent; upper glumes as long as the lower lemmas, 5-7-veined; lower lemmas 3-5-veined; upper florets 2.5-3 mm long, 1.4-1.8 mm wide, dark glossy brown. Caryopses 1.1-1.5 mm, nearly orbicular. 2n = 20, 40, 60, 120.
(Description source: Barkworth, M.E., Capels, K.M., Long, S. & Piep, M.B. (eds.) 2003. Flora of North America, north of Mexico. Volume 25. Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Poaceae, Part 2. Oxford University Press, New York. 783 pp http://floranorthamerica.org/Paspalum_scrobiculatum )
Perennials; culms tufted, stout, erect, 6- 12 dm tall, glabrous, somewhat bulbous at base. Sheaths 7-14 cm long, glabrous or sometimes sparsely long-hispid at throat, somewhat compressed, basal ones often purple-tinged, usually with minute membranous auricles; ligule membranous, 1-1.5 mm long with a dense row of hairs 1-2 mm long behind it; blades flat, erect or ascending, 12-40 cm long, 3-12 mm wide, scabrous, upper surface glaucous, the midrib conspicuous on lower surface, apex acute. Racemes 4-6, widely spaced, alternate, spreading, 2-4 cm long, villous at base, glabrous or sparsely long-pilose in the axils, the axis 4-9 cm long, rachis 1-1.5 mm wide, scabrous, margins usually red; spikelets solitary or paired, closely imbricate, broadly elliptic, 2-2.5 mm long, ca. 1.5 mm wide, glabrous; second glume and first lemma 3- nerved, midnerve distinct, marginal nerves faint; second lemma brown, cartilaginous, indurate, slightly shorter than second glume and first lemma, strongly convex, finely punctate; palea nerveless or 2- nerved, similar to lemma. Caryopsis whitish, broadly elliptic, compressed, ca. 1.5 mm long. [2n = 20, 40, 42, 50, 54, 60, 80, ca. 90, 120.]
(Description source: O’Connor, P.J. 1990. Poaceae, pp. 1481–1604. In: Wagner W.L., Herbst D.R. & Sohmer S.H. (eds.)., Manual of the flowering plant of Hawaiʻi. Vol. 2. University of Hawaii Press & Bishop Museum Press, Honolulu )