Info
Subfamily: Chloridoideae
Genus etymology: Enneapogon = "nine beard" [Greek] refering to the lemma having nine hairy awns
Species etymology: cenchroides = "resembling Cenchrus L." [Greek] refering to the inflorescence
Photosynthetic type: C4 (warm season)
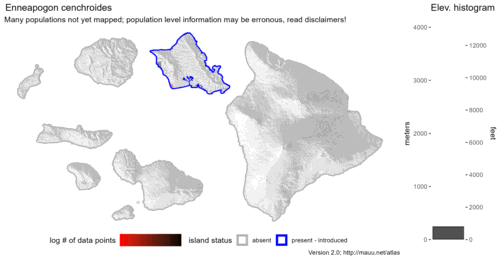
Nativity: naturalized - accidental
First recorded in Hawaiʻi: 2023
Map
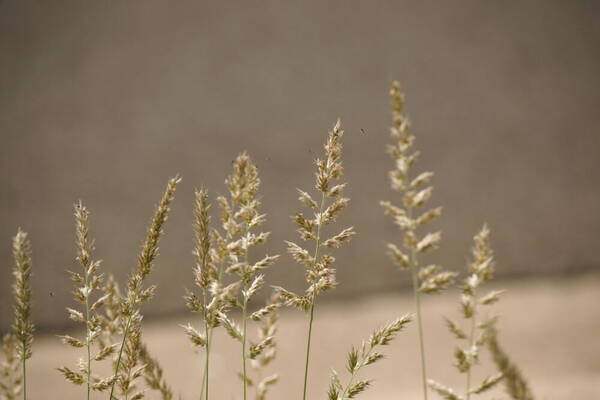
Inflorescence
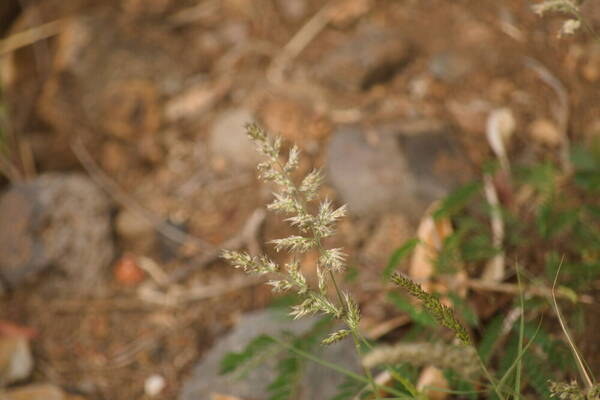
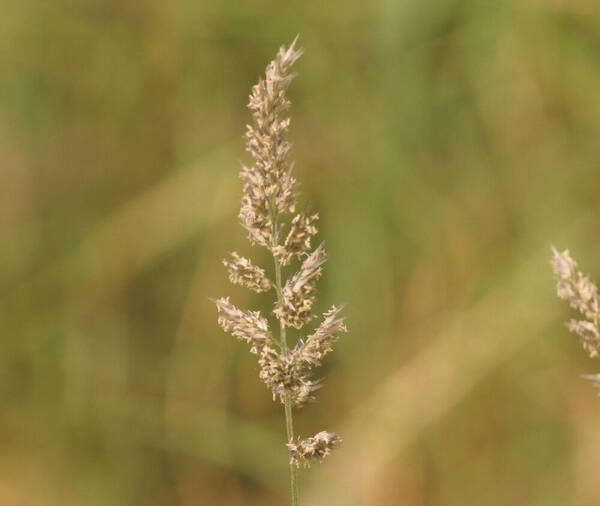



Plant
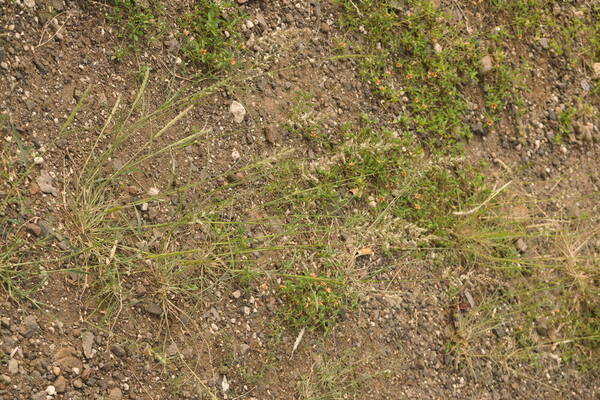

Habit
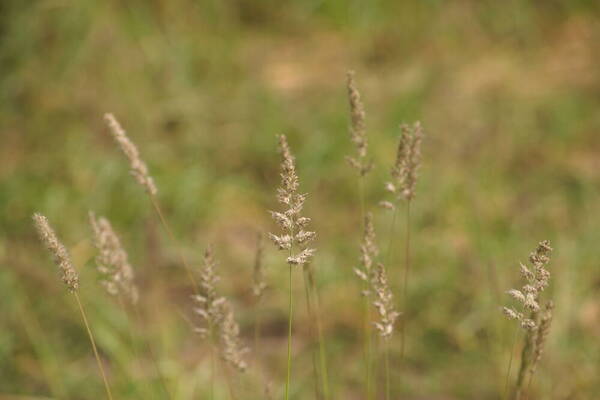
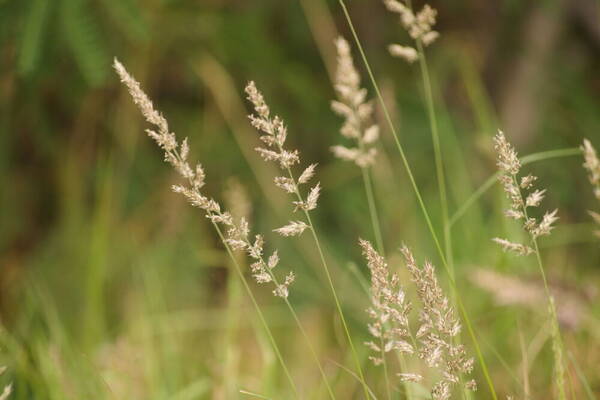
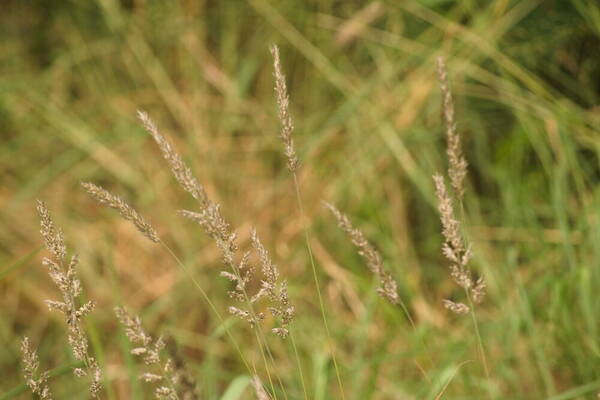
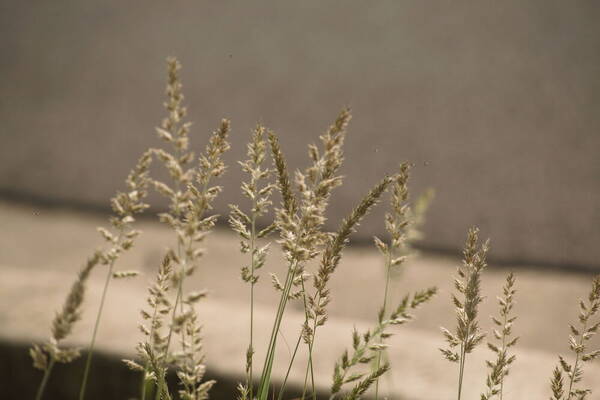
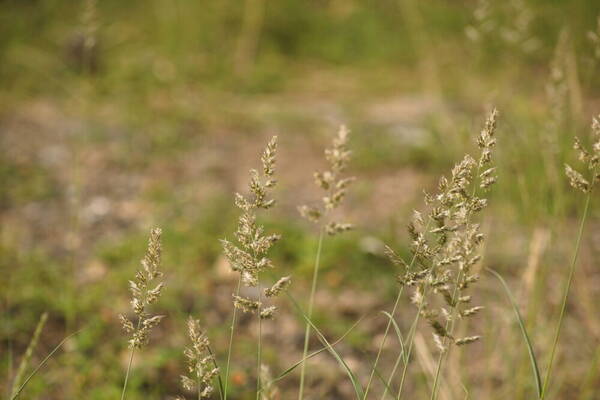





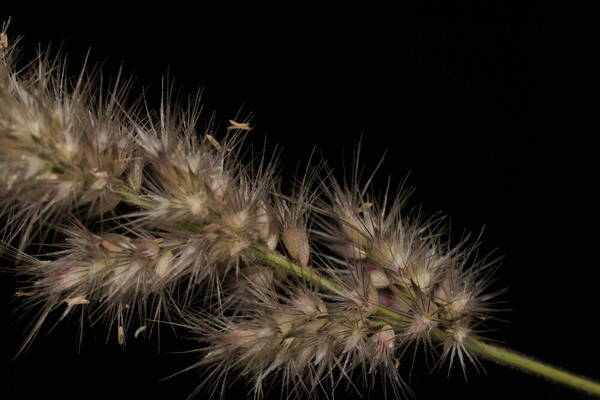
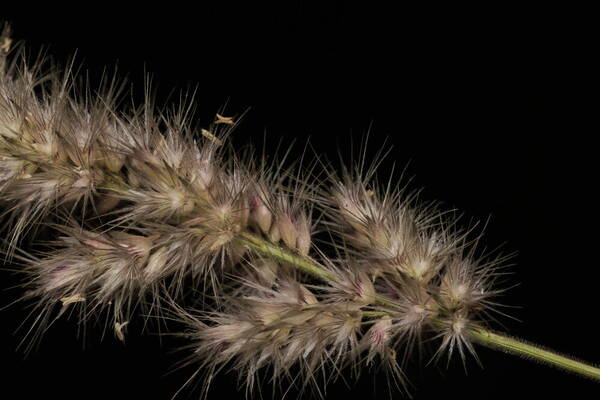
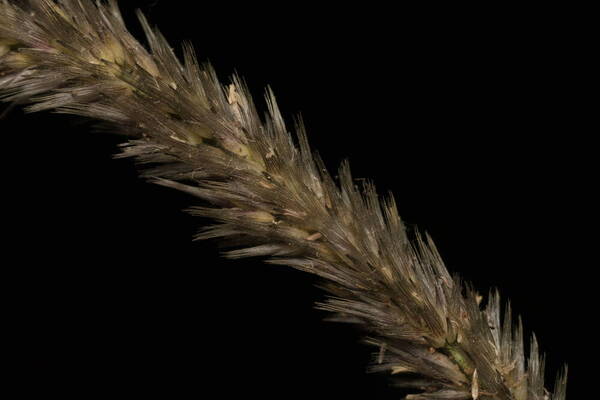
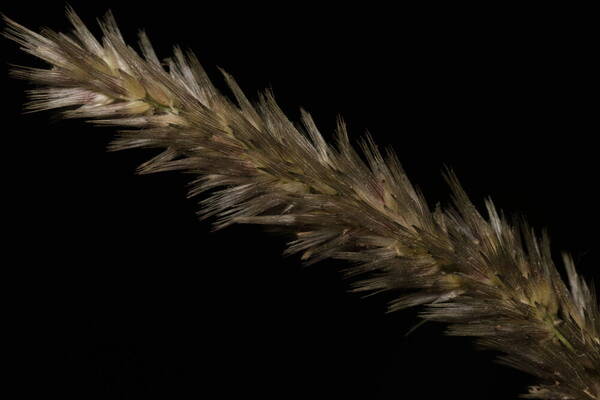
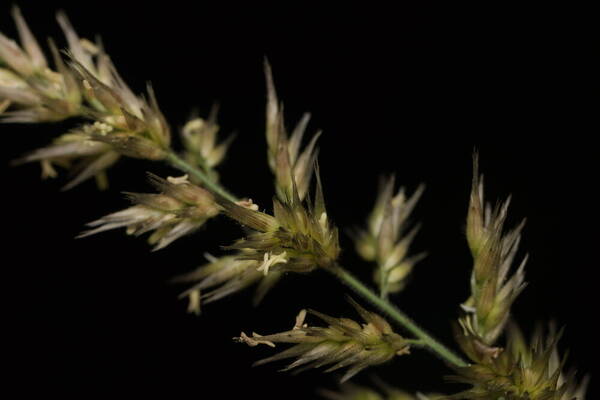
Spikelets
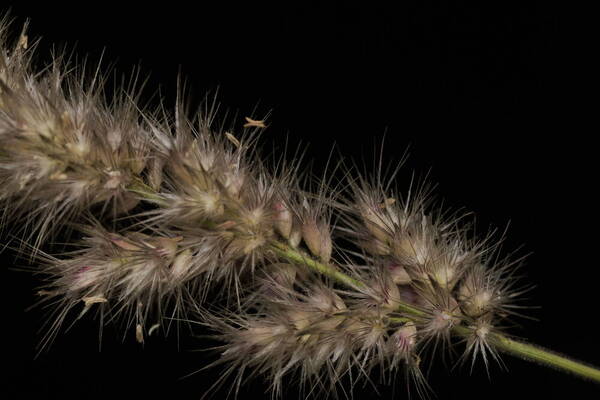
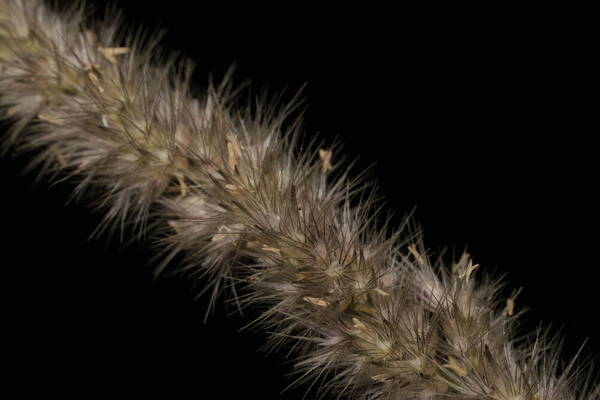







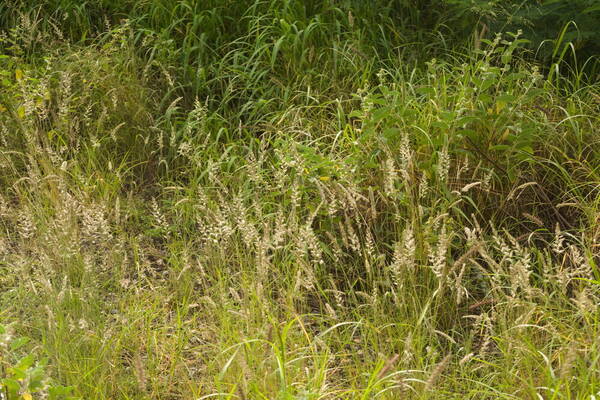
Landscape


Description
Tufted robust annual often assuming a perennial appearance; culms wiry below, up to 1 m. high, usually shortly hairy all over. Leaf-blades up to 25 cm. long and 7 mm. wide, involute or flat. Inflorescence a contracted or spike-like panicle up to 16 cm. long. Lower glume 3–4 mm. long, 5–7-nerved; upper glume 3.5–5.5 mm. long, 3-nerved; lowest lemma 1.5–2 mm. long, its awns 2.5–5 mm. long and densely ciliate for much of their length; second lemma smaller, usually ♂; third lemma 0.7–2 mm. long, including the awns which are reduced to a small tuft; anthers 1–1.8 mm. long. Fig. 55/1–8.
(Description source: Clayton, W.D. 1970. Flora of Tropical East Africa. Gramineae (Part 1). Crown Agents for Oversea Governments and Administrations, London. 176 pp. )
Annual up to 75 cm high; basal sheaths remaining intact. Panicle loosely contracted, often lobed at the base. Lower glume 5- to 7-nerved, 2.6–3.8 mm long; upper glume 3-nerved, 3.5–5 mm long; fertile lemma 4–7 mm long (including awns), hairy on the back all over; awns ciliate; anthers 1–1.7 mm long; third lemma vestigial, occasionally well developed (but barren), 0.3–2(–3.5) mm long.
(Description source: Cope, T.A, (1995) Flora Somalia, Vol 4. Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew, London. 312 pp. )
A loosely caespitose annual or rarely shortly lived perennial, densely glandular-pubescent all over. Culms 15-100 cm. tall, 2-5-noded, rather stout, geniculately ascending, seldom erect, sometimes decumbent, simple or branched below. Leaf-sheaths relatively tight, usually slightly shorter than the internodes, striate, smooth or somewhat asperulous towards the mouth. Leaf-laminae 3-25 x (0.1)0.3-0.7(1) cm., linear to lanceolate-linear, long-tapering to a fine point, expanded or convolute (often only towards the apex), rigid to subflaccid, scaberulous on the upper surface and along the margins. Panicle 3-15(20) cm. long, spike-like, usually dense and contracted, rarely somewhat open below, compact, rarely interrupted. Spikelets 3-5 mm. long, usually crowded, 3-flowered. Glumes slightly unequal, light to dark grey or grey-green; the inferior 2.8-4(5.1) mm. long, 5-7-nerved, ovate; the superior 3.2-5.5(6.8) mm. long, 3-nerved, oblong, often with the apex somewhat truncate. Fertile lemma (the inferior) 1.5-2 mm. long (excluding the awn), dorsally shortly villous; awns 3-4.25 mm. long, plumose up to or beyond the middle. Palea 2-2.25 mm. long, with the keels ciliolate. Anthers 0.8-1.8(2.3) mm. long.
(Description source: Launert, E. & Pope, G.V. (eds.). 1989. Flora Zambesiaca. Volume 10. Part 3. Kew, London. 152 pp )
A loosely caespitose annual or rarely shortly lived perennial, densely glandularpubescent all over. Culms 15–100 cm. tall, 2–5-noded, rather stout, geniculately ascending, seldom erect, sometimes decumbent, simple or branched below. Leafsheaths relatively tight, usually slightly shorter than the internodes, striate, smooth or somewhat asperulous towards the mouth. Leaf-laminae 3–25 × (0.1)0.3–0.7(1) cm., linear to lanceolate-linear, long-tapering to a fine point, expanded or convolute (often only towards the apex), rigid to subflaccid, scaberulous on the upper surface and along the margins. Panicle 3–15(20) cm. long, spike-like, usually dense and contracted, rarely somewhat open below, compact, rarely interrupted. Spikelets 3–5 mm. long, usually crowded, 3-flowered. Glumes slightly unequal, light to dark grey or grey-green; the inferior 2.8–4(5.1) mm. long, 5–7-nerved, ovate; the superior 3.2– 5.5(6.8) mm. long, 3-nerved, oblong, often with the apex somewhat truncate. Fertile lemma (the inferior) 1.5–2 mm. long (excluding the awn), dorsally shortly villous; awns 3–4.25 mm. long, plumose up to or beyond the middle. Palea 2–2.25 mm. long, with the keels ciliolate. Anthers 0.8–1.8(2.3) mm. long.
(Description source: Fernandes, A., Launert, E. & Wild, H. (eds.). 1971. Flora Zambesiaca. Volume 10. Part 1. Crown Agents, London. 152 pp. )